I am a PhD student at the University of New South Wales, supervised by of Dr. Hammond Pearce and Dr. Jason Xue. My research is supported by the UNSW UIPA Scholarship and CSIRO’s Data61 Top-up Scholarship, focusing on vulnerablities of AI models.
My research interest includes AI security and safety, multi-modal models and embodied robotics. I have published several papers at the top international AI and security conferences (e.g. CCS, S&P, Usenix, NDSS, WWW) with total google scholar citations 100+. I am also honored with the Google PhD Fellowship, 2025.
🔥 News
- 2025.10: 🎉 Awarded the Google PhD Fellowship!
- 2025.10: 🎉 Our poster for “What’s Pulling the Strings? Evaluating Integrity and Attribution in AI Training and Inference through Concept Shift” received RAID 2025 (core A) best poster award.
- 2025.08: 🎉 Awarded the CCS conference grant.
- 2025.05: 🎉 Our paper titled “What’s Pulling the Strings? Evaluating Integrity and Attribution in AI Training and Inference through Concept Shift” was accepted by CCS 2025!
- 2024.04: 🎉 Our paper titled “LACMUS: Latent Concept Masking for General Robustness Enhancement of DNNs” was accepted by S&P 2024!
- 2024.04: 🎉 Our paper titled “{DNN-GP}: Diagnosing and Mitigating Model’s Faults Using Latent Concepts” was accepted by Usenix 2024!
- 2023.11: 🎉 Our paper titled “A duty to forget, a right to be assured? exposing vulnerabilities in machine unlearning services” was accepted by NDSS 2024!
- 2023.03: 🎉 Our paper titled “Copyright protection and accountability of generative ai: Attack, watermarking and attribution” was accepted by WWW 2024!
📝 Publications

What’s Pulling the Strings? Evaluating Integrity and Attribution in AI Training and Inference through Concept Shift Link
Jiamin Chang, Haoyang Li, Hammond Pearce, Ruoxi Sun, Bo Li, Minhui Xue
- To assess and attribute trustworthiness threats, we propose ConceptLens, a generic framework that leverages pre-trained multimodal models to identify the root causes of integrity threats by analyzing Concept Shift in probing samples. ConceptLens demonstrates strong detection performance for vanilla data poisoning attack and identifies privacy risks in unaltered but high-risk samples, and provides insights into model weaknesses arising from incomplete or imbalanced training data. Additionally, it attributes concepts that the target model is overly dependent on, identifies misleading concepts, and explains how disrupting key concepts negatively impacts the model. Furthermore, it uncovers sociological biases in generative content, revealing disparities across sociological contexts.

LACMUS: Latent Concept Masking for General Robustness Enhancement of DNNs Link
Shuo Wang, Hongsheng Hu, Jiamin Chang, Benjamin Zi Hao Zhao, Minhui Xue
- We present LAtent Concept Masking for robUStness (LACMUS), a novel perceptually-driven methodology that enhances DNN robustness without requiring prior knowledge about the adversarial contexts. We argue that DNNs’ sensitivity to adversarial perturbations and distribution drifts stems from overfitting to non-common concepts within the dataset, leading to an over-reliance on specific learned instances and increased vulnerability. LACMUS addresses this by mapping high-dimensional data into a latent conceptual space to identify and navigate patterns of “non-common concepts” within the latent concept space.
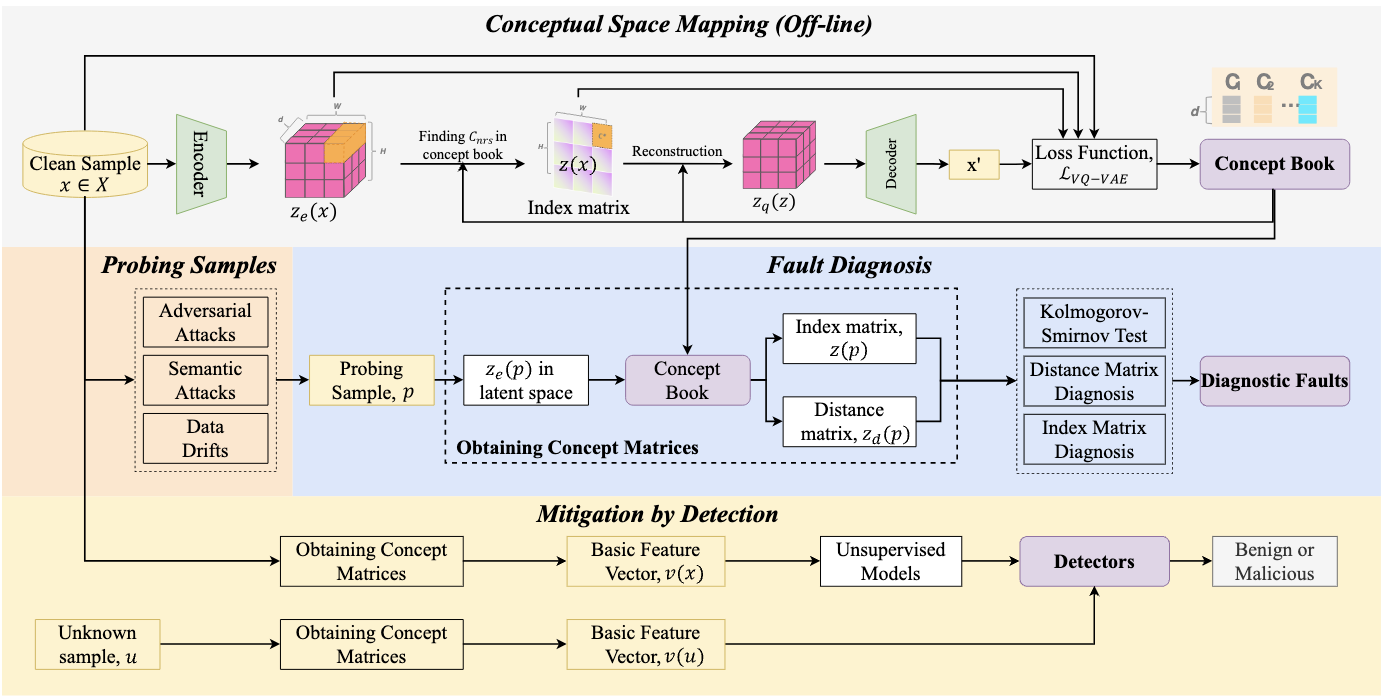
{DNN-GP}: Diagnosing and Mitigating Model’s Faults Using Latent Concepts Link
Shuo Wang, Hongsheng Hu, Jiamin Chang, Benjamin Zi Hao Zhao, Qi Alfred Chen, Minhui Xue
- We present a fault diagnosis tool (akin to a General Practitioner) DNN-GP, an integrated interpreter designed to diagnose various types of model faults through the interpretation of latent concepts. DNN-GP incorporates probing samples derived from adversarial attacks, semantic attacks, and samples exhibiting drifting issues to provide a comprehensible interpretation of a model’s erroneous decisions. Armed with an awareness of the faults, DNN-GP derives countermeasures from the concept space to bolster the model’s resilience.
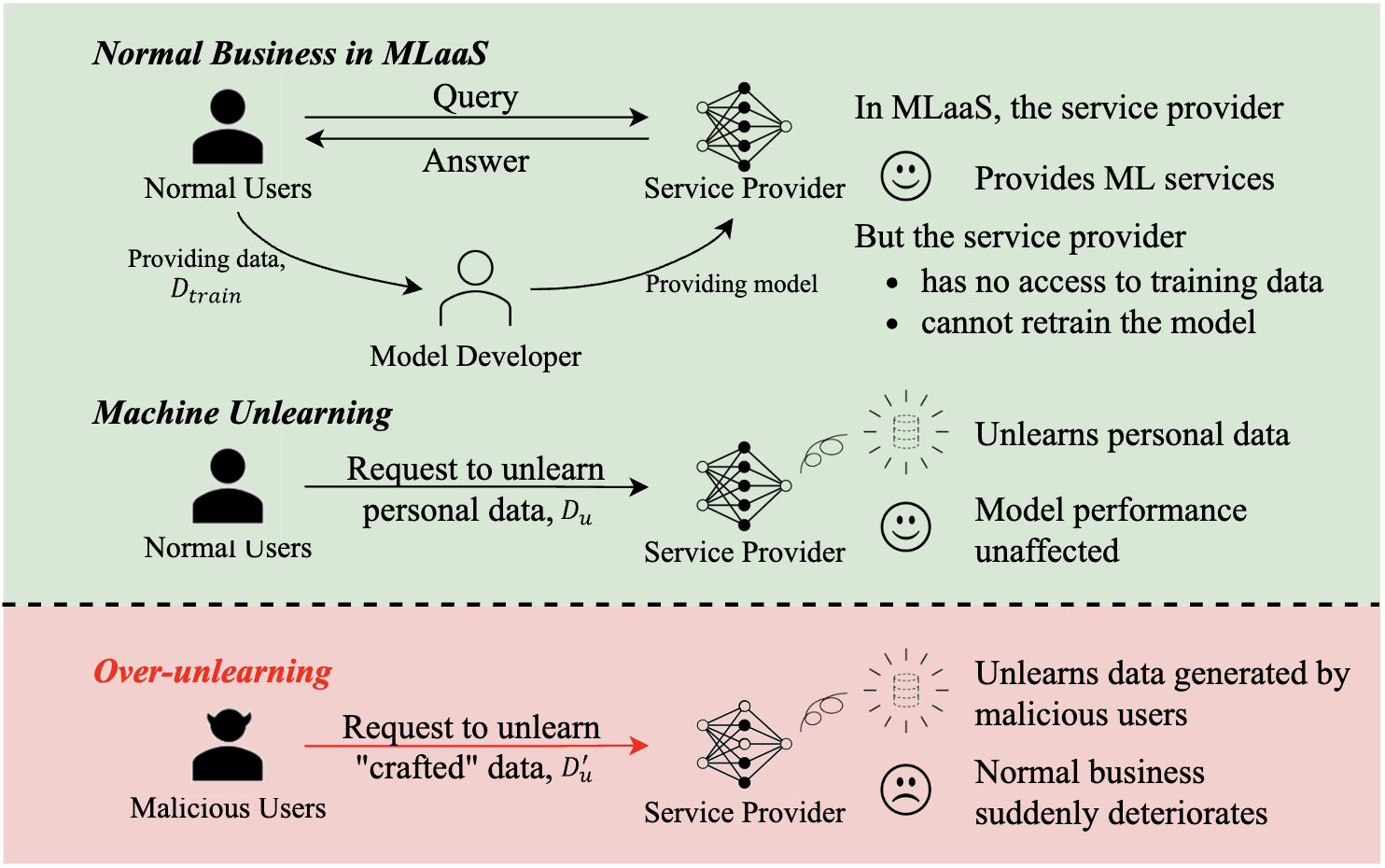
A duty to forget, a right to be assured? exposing vulnerabilities in machine unlearning services Link
Hongsheng Hu, Shuo Wang, Jiamin Chang, Haonan Zhong, Ruoxi Sun, Shuang Hao, Haojin Zhu, Minhui Xue
- We try to explore the potential threats posed by unlearning services in MLaaS, specifically over-unlearning, where more information is unlearned than expected. We propose two strategies that leverage over-unlearning to measure the impact on the trade-off balancing, under black-box access settings, in which the existing machine unlearning attacks are not applicable. The effectiveness of these strategies is evaluated through extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, across various model architectures and representative unlearning approaches.
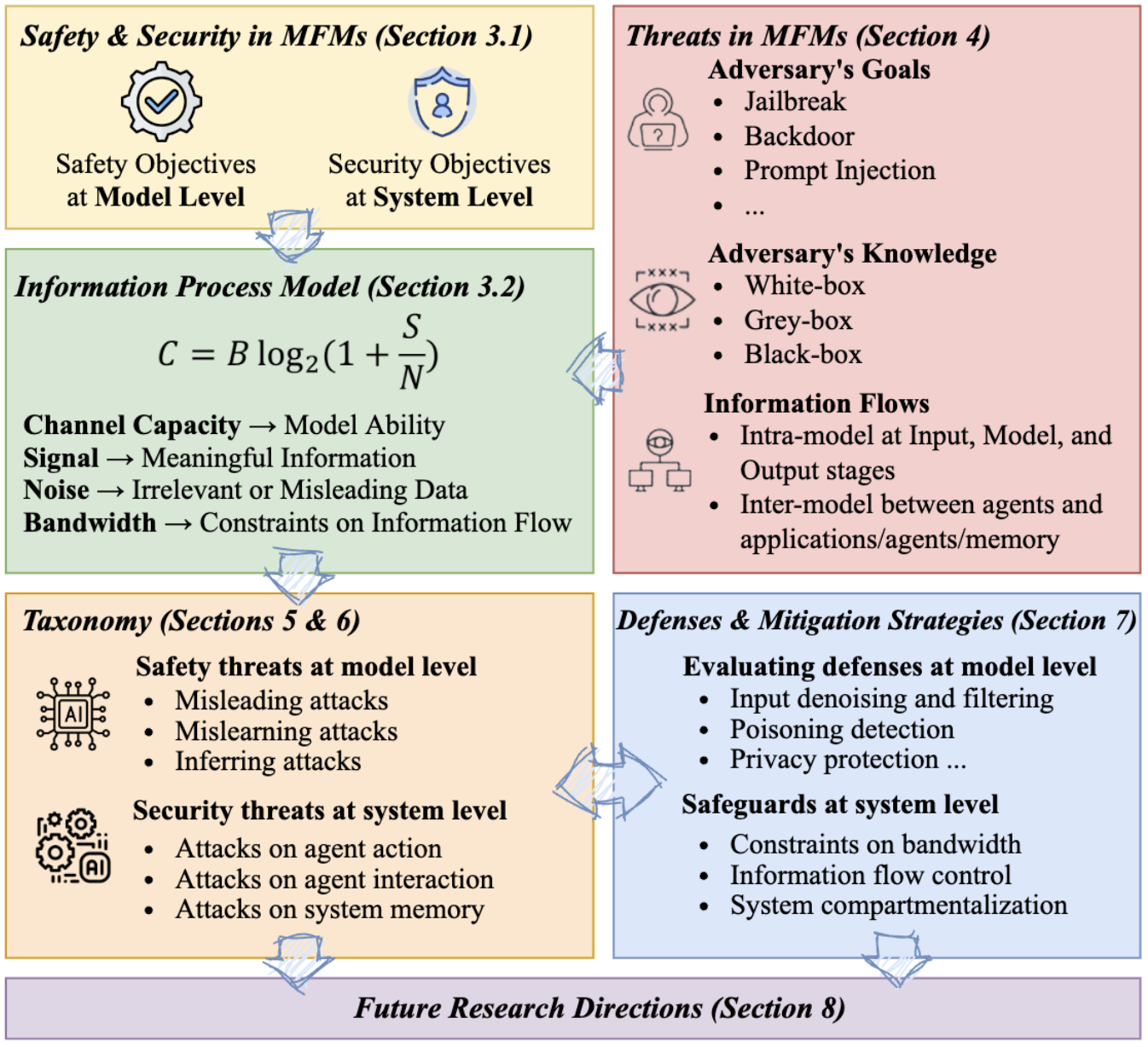
SoK: Unifying Cybersecurity and Cybersafety of Multimodal Foundation Models with an Information Theory Approach Link
Ruoxi Sun, Jiamin Chang, Hammond Pearce, Chaowei Xiao, Bo Li, Qi Wu, Surya Nepal, Minhui Xue
- We conceptualize cybersafety and cybersecurity in the context of multimodal learning and present a comprehensive Systematization of Knowledge (SoK) to unify these concepts in MFMs, identifying key threats to these models. We propose a taxonomy framework grounded in information theory, evaluating and categorizing threats through the concepts of channel capacity, signal, noise, and bandwidth. This approach provides a novel framework that unifies model safety and system security in MFMs, offering a more comprehensive and actionable understanding of the risks involved.
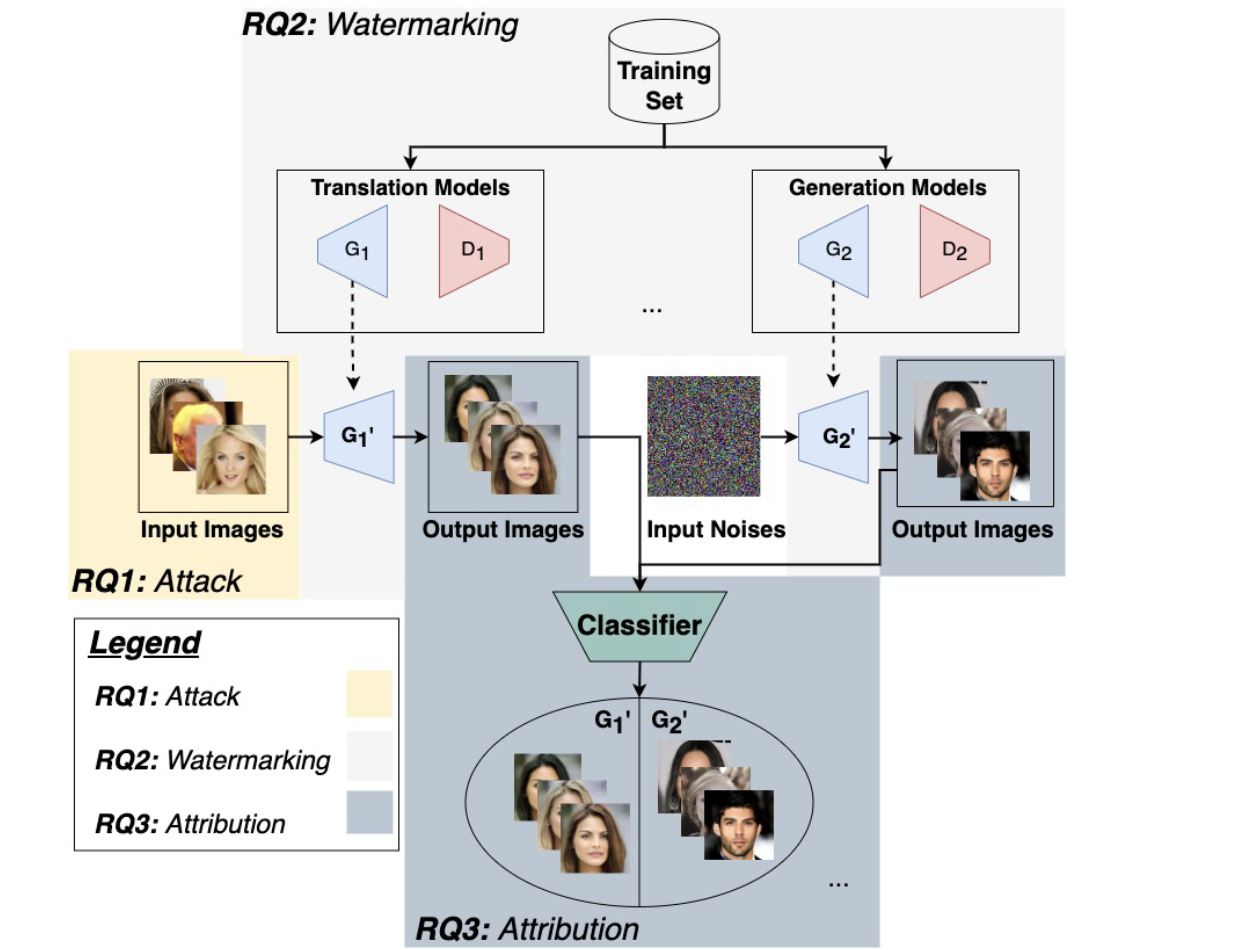
Copyright protection and accountability of generative ai: Attack, watermarking and attribution Link
Haonan Zhong, Jiamin Chang (Co-first Author), Ziyue Yang, Tingmin Wu, Pathum Chamikara Mahawaga Arachchige, Chehara Pathmabandu, Minhui Xue
- We propose an evaluation framework to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of the copyright protection measures for GANs, evaluate their performance across a diverse range of GAN architectures, and identify the factors that affect their performance and future research directions. Our findings indicate that the current IPR protection methods for input images, model watermarking, and attribution networks are largely satisfactory for a wide range of GANs.
🎖 Honors and Awards
- 2025.10 Google PHD Fellowship
- 2025.10 RAID 2025 Best Poster Award
- 2025.08 CCS Student Conference Grant
- 2024.04 Csiro Data61 PHD Top-up Scholarship
- 2023.03 Csiro Data61 CSCRC Honors Scholarship
- 2021.09 Faculty of Engineering Taste of Research Scholarship
- 2020.06 UNSW Global Academic Award
📖 Educations
- 2024.05 - NOW, UNSW, Doctor of Philosopy, Computer Science
- 2023.02 - 2024.03, UNSW, Honors of Engineering, Computer Science and Engineereing. Grade: 90.75 HD & First Class Honors
- 2020.06 - 2023.02, UNSW, Bachelor of Engineering, Computer Science. Grade: 88.042 HD & 2021/2022/2023 Dean’s Honours List (Highly Recommend)
